Posts
One to Watch: S2G BioChem
/in Uncategorized/by Green Coast RubbishWith global warming on the rise, companies offering clean energy and biochemical solutions are leading the way in both innovation and sustainability. Green Coast Rubbish would like to highlight one such company to watch – S2G BioChem – in this week’s blog.
What they do: S2G BioChem produces glycols for the industrial chemical industry without using petroleum products.
Glycols are used to produce many common household products such as liquid detergents, lotions, personal care products, car antifreeze, plastics, packaging material and many other common household products. This is a $30 billion dollar industry.
Environmental benefits: Glycols are typically made from petroleum products (ethylene, propylene, naptha) which are associated with rising GHG emissions and global warming.
In contrast, S2Gs bio-glycols are made from low cost, sustainable, non-food based agriculture and forestry waste products which reduces green house gas emissions by an estimated 1.8 tonne of C02 equivalent per tonne of glycol produced. According to S2G’s website, converting even just 5% of the current glycol market to bio-glycols would take the equivalent of 330,000 cars off the road or about 1,800 kilotonnes each year.
We work with them: In 2014, Green Coast Rubbish helped S2G remove and treat over 26,000 litres of waste water from their Vancouver based pilot plant (all of which is derived from plants and biological feedstock) and also recycled much of their construction waste.
Why we like them: “We are a big fan of S2G because of their use of renewable plant based sources in place of conventional fossil fuel feedstocks, and more importantly they are a great group of individuals to work with,” says Green Coast Rubbish President Eamonn Duignan.
Learn more: To find out more information about S2G BioChem, visit their website.
My Funny Valentine Recycling No No’s
/in community, composting, Electronics Recycling, Organic Waste, Recycling/by Green Coast Rubbish If you are in a relationship or just want to pamper a loved one, February 14 is the day to make your funny Valentine smile with their heart. No matter what you do or where you go for Valentine’s Day, you can make it special while keeping it green by remembering a few recycling no nos.
If you are in a relationship or just want to pamper a loved one, February 14 is the day to make your funny Valentine smile with their heart. No matter what you do or where you go for Valentine’s Day, you can make it special while keeping it green by remembering a few recycling no nos.
What to do: Treat your loved one to a selection of hand dipped chocolate covered strawberries.
Recycling no no: Don’t forget to compost any leftovers and the strawberry stems.
Where to go: Take her out for a surprise Valentine’s overnight getaway at a fancy hotel or resort.
Recycling no no: Skip the hotel water bottles and drink out of the tap.
What to do: Plan and cook your sweetheart a romantic meal.
Recycling no no: Food scraps don’t go in the garbage. All organics should be composted or recycled in your yard or garden bin.
What to do: Set a romantic mood with music, candles and a glass of wine.
Recycling no no: Cork the bottle if you don’t finish drinking all the wine and save it for another day. Don’t toss the bottles; these can be returned for change at your local Return It Depot.
Where to go: If cooking isn’t your thing, do book a reservation at her favourite restaurant.
Recycling no no: Don’t leave your doggie bag in the car when you get home. That’s a total waste of good breakfast food not to mention the unnecessary use of packaging.
What to do: If your sweetie specifically asks for a new Kobo or smart watch for Valentine’s Day, then knock yourself out but skip the coffee bean grinder unless you want to see her grinding her teeth.
Recycling no no: Unless you’ve been hiding under a rock, you’ll know that all electronics may be dropped off at an appropriate facility for recycling.
What to do: Flowers will melt your loved one’s heart – roses, mixed bouquets or potted orchids may be just the ticket.
Recycling no no: Skip the dyed blue roses and remember to compost the wilted remnants in a week or two.
What to do: Remember! Valentine’s Day is February 14.
Recycling no no: Mark it on your calendar or you’ll be recycling excuses for years to come.
Clean Wood: Recycle it or Pay the Price
/in composting, Organic Waste, Recycling, Renovation Waste/by Green Coast RubbishAs Metro Vancouver moves toward the goal of recycling 80% of the region’s waste by 2020, new rules are being implemented to divert green waste from the garbage including the organics disposal ban we talked about last week as well as a new clean wood disposal ban effective January 1, 2015.
What is Clean Wood?
For the purposes of the ban, clean wood includes solid wood, lumber and pallets that are unpainted, unstained, untreated and glue free. It’s okay if the wood contains nails, screws, staples or other metal fasteners.
Important Dates and Phases
The first 6 months of the ban -January 1 to June 30, 2015 – will focus on educating customers at all regional facilities including transfer stations and landfills about the clean wood disposal ban. As of July 1, 2015, loads of garbage containing over 10% clean wood will be subject to a 50% surcharge.
Recycle it or Pay the Price
You’ll save money and the environment by recycling clean wood:
1. Recycled clean wood can be used for composting, landscaping mulch or alternative industrial fuel.
2. The fee to recycle clean wood at a Metro Vancouver facility costs less than the garbage disposal fee, not to mention having to pay the price of the 50% surcharges as of July 1.
Why we Like It
Green Coast Rubbish is fully on board with the ban and is already recycling clean wood products as part of its every day operations. In 2013, Green Coast Rubbish composted 30.39 tonnes of clean wood and organic material.
Eamonn Duignan, President of Green Coast Rubbish explains, “It is encouraging to see clean wood being banned from Metro Vancouver facilities, especially when this material can be easily be composted or recycled. As material recovery options increase and become more economical viable within our region, we hope to see an outright ban of all wood products in the not so distant future.”
Who to Contact
For more information on the clean wood disposal ban, call the Recycling Council of BC’s Recycling Hotline at 604-RECYCLE (604-732-9253) or contact your local municipality.
Organics Disposal Ban Launches in Metro Vancouver
/in Commercial Rubbish Removal and Recycling, composting, Organic Waste, Recycling/by Green Coast RubbishRecycling food scraps is routine for many Metro Vancouver residents and businesses. However, the new organics disposal ban in effect as of January 1, 2015 now requires all households, businesses, and institutions to separate food waste from their garbage.
Why the ban? You may be surprised to learn that almost a third of the food we buy ends up in the garbage, amounting to 40% of residential garbage in the landfill. This slowly decaying food creates methane gas which is known to cause global warming.
While the majority of single family homes in Metro Vancouver are already recycling food and garden waste, the organics disposal ban will ensure that residential buildings (such as apartments and condos) are starting food scrap recycling programs if they haven’t already done so. Another major focus for the ban this year is to ensure that large restaurants and grocery stores are diverting organics from their garbage.
In summary, all residents, businesses and institutions are being asked to introduce food scraps recycling programs this year to meet the regional goals of recycling 70% of the waste in Metro Vancouver in 2015 and 80% by 2020.
Important Dates and Phases
The organics disposal ban is being introduced in stages over the coming months and includes an educational focus for the first 6 months, followed by the implementation of financial penalties in the latter half of 2015 as follows:
What Items are Banned?
Food scraps recycling programs should include the following items which are now banned from the garbage:
• Vegetables and fruits
• Raw food, plate scrapings, leftovers
• Packaged foods (remove packaging)
• Meats, fish, bones and seafood shells
• Pasta, bread and rice
• Dairy, eggshells, sauces, dressings
• Paper egg cartons
• Paper towels, unlined paper cups/plates
• Food-soiled napkins/pizza boxes/newspaper
• Kraft/paper bags used to collect food scraps
• Waxed cardboard boxes
• Coffee grounds/filters and tea bags
• Wooden utensils, chopsticks, stir sticks, and toothpicks
Resources
For more information on the organics disposal ban, check out the following links:
The Recycling Council of BC is available to answer questions and provides information on food scraps recycling programs and contacts for commercial and multi-family dwelling organics pick-up services. Call 604-RECYCLE (604-732-9253).
Metro Vancouver Organics Ban: Overview
Businesses: Q&A on Metro Vancouver’s Organics Disposal Ban
Restaurants : Tools and Resources, Case Studies, Frequently Asked Questions, Tips, Signage & Artwork
Grocers: Tools and Resources, Case Studies, Frequently Asked Questions, Tips, Signage & Artwork
Apartments & Condos: Tools and Resources, Case Studies, Frequently Asked Questions, Tips, Signage and Artwork
Residents: Tools and Resources, Case Studies, Frequently Asked Questions, Tips and Posters
Recycling Resources in Metro Vancouver and BC
/in Recycling/by Green Coast RubbishIt’s not unusual to feel a little like Sherlock Holmes when you are trying to figure out where in the world to recycle or dispose of your old stuff. You can use basic deductive reasoning and call your local municipality or recycling centre to try and get some answers. You can just pile up your old TV, propane cannisters, paint cans and other old stuff in the back of your garage in the hopes that it will magically disappear (or call Green Coast Rubbish to come and recycle it for you!). Or like Sherlock Holmes, you can do some “elementary” research using one of these great recycling resources to solve even the most puzzling recycling mysteries.
1. BC Recyclepedia Smart Phone App
We like this handy little app which offers recycling options throughout British Columbia for over 70 materials. Select the item(s) you want to recycle or dispose of from the pick list and you will receive a list of the 10 nearest depot’s and a Google map with directions. Download this free app onto your iPhone or Android device or view the same information on the Recyclepedia web page.
2. Metro Vancouver Recycles
Residents and businesses can visit the Metro Vancouver Recycles web page to find places to donate or recycle just about anything. You will be asked to select the material you wish to recycle or dispose of and provide your location information to get a list of suitable recycling options.
3. North Shore Recycling – Recycling Directory
If you live on the North Shore you are probably already familiar with North Shore Recycling; however their recycling directory is a great resource for all Metro Vancouver residents. This extensive directory describes where you can recycle your items as well as connecting you with detailed information on provincial stewardship programs and other resources.
4. Recycling Hotline
When all else fails and you can’t solve the mystery of where to take your items for recycling, the Recycling Council of British Columbia’s Recycling Hotline is the place to call. You’ll find an expert at the end of the line who will be able to do the detective work for any recycling or disposal mysteries you may be experiencing. Call 604-RECYCLE; 604-732-9253; or 1-800-667-4321 or email hotline@rcbc.ca.
5. Sell or Donate It
Sell or donate your reusable stuff to others using one of a variety of local websites such as:
- Habitat for Humanity Greater Vancouver
- Craigslist Vancouver
- Used Vancouver
- Helping Families in Need Society
- Kijiji Vancouver
No mystery here Watson. Just some good old fashioned detective work!
Deconstructing Vancouver’s Green Demolition Bylaw
/in Recycling/by Green Coast RubbishHome owners and property developers in the city of Vancouver will follow new demolition waste recycling requirements for houses built before 1940 thanks to the Green Demolition Bylaw which went into effect on September 1, 2014. From now on, a minimum of 75% of the demolition waste from these older homes will be recycled; and that number increases to 90% for character houses from the same era.
We had the opportunity to interview Senior Sustainability Specialist Hugo Haley from the City of Vancouver to find out more about the Green Demolition Bylaw and what it means for home owners and developers. Here’s what he was able to share with us:
Q: What led the City of Vancouver to establish these new recycling requirements for pre-1940’s houses?
A: Metro Vancouver’s regional solid waste plan requires all municipalities to do more to encourage recycling of construction and demolition waste. Also, the City of Vancouver’s Greenest City Action Plan’s Zero Waste goal is to reduce the amount of solid waste disposed to landfill by 50% by 2020. To achieve this goal, the City intends to improve demolition waste recycling performance, and put in place policies to achieve 50,000 tonnes additional recycling from the demolition and construction waste sector.
Q: What is the difference between a pre-1940’s home to one that was built later that prompted this policy? Will newer home demolitions become subject to similar recycling requirements in the future?
A: Homes built before 1940 often have valuable architectural features … built with old growth timber and other valuable materials. The City would like to discourage older character homes from being demolished … if they are going to be demolished, the City wants to ensure that a high percentage of demolition materials are reused or recycled. In the future, the City would like to include recycling requirements for all ages classes of homes to make sure valuable and usable materials are kept out of the landfill.
Q: What is “deconstruction” and why is it being used to demolish these older homes?
A: Deconstruction is an alternative to traditional demolition. Deconstruction is a more systematic and careful approach to taking apart the house where more of the materials are kept intact and can then be separated for reuse and recycling.
Q: Is this new bylaw unique in Metro Vancouver, perhaps even in North America?
A: These requirements are not unique in North America. There are numerous municipalities in the United States that require demolition waste recycling, with California’s requirements applying state wide. Cities with similar policies include Chicago, Seattle, San Fransicso and Boulder. In Metro Vancouver, the city of Port Moody has such a policy.
Q: Do you have any relevant statistics you can share including how many demolitions and how much material you think will be diverted from the landfill each year?
A: There are about 1,000 homes demolished in the city of Vancouver every year. About 350 of those are from the pre-1940 era and subject to the new requirements. We expect about 12,000 tonnes of additional reuse and recycling to be achieved in the first year … This amount will increase as the requirements extend to more homes.
Green Coast Rubbish President & CEO Eamonn Duignan wrote a letter to Council in support of the new bylaw saying “we whole heartily support this policy initiative … far too often we see reusable or recyclable material landfilled, simply because there is no regulatory framework in place.”
Green Coast Rubbish specializes in demolition and deconstruction services.
If you are considering the deconstruction of a pre-1940’s home, here are some helpful links for more information:
- City Bulletin – Demolition Permits for Pre-1940 Houses – Waste Recycling Requirements
- City of Vancouver Recycling requirements for your demolition project
- City of Vancouver Demolition permit with recycling requirements
- Metro Vancouver’s Demolition, Land Clearing and Construction Waste Management Toolkit
- Bulletin: Heritage or Character Building Review – Interim Procedure
Pacific Carpet Recycling
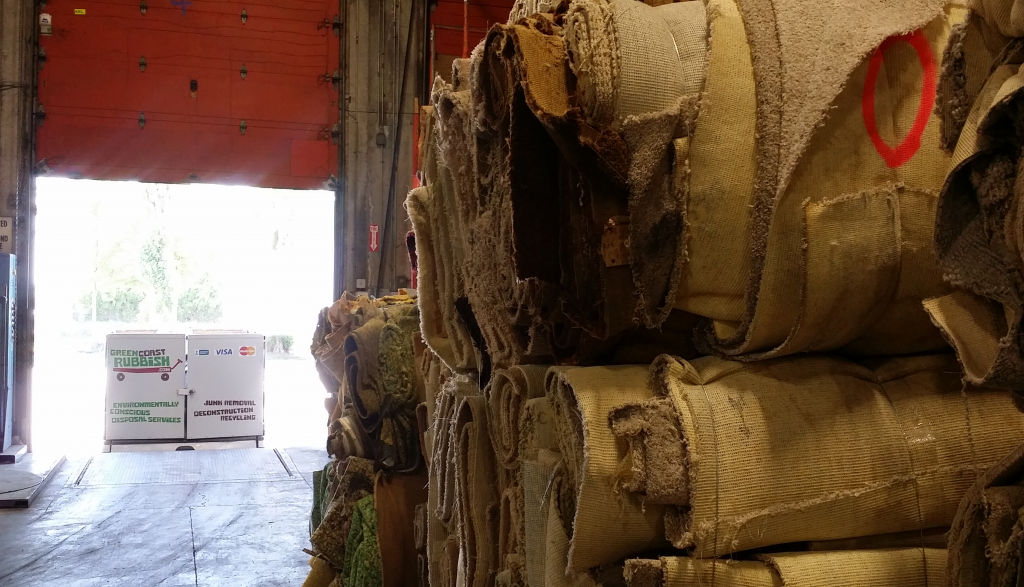
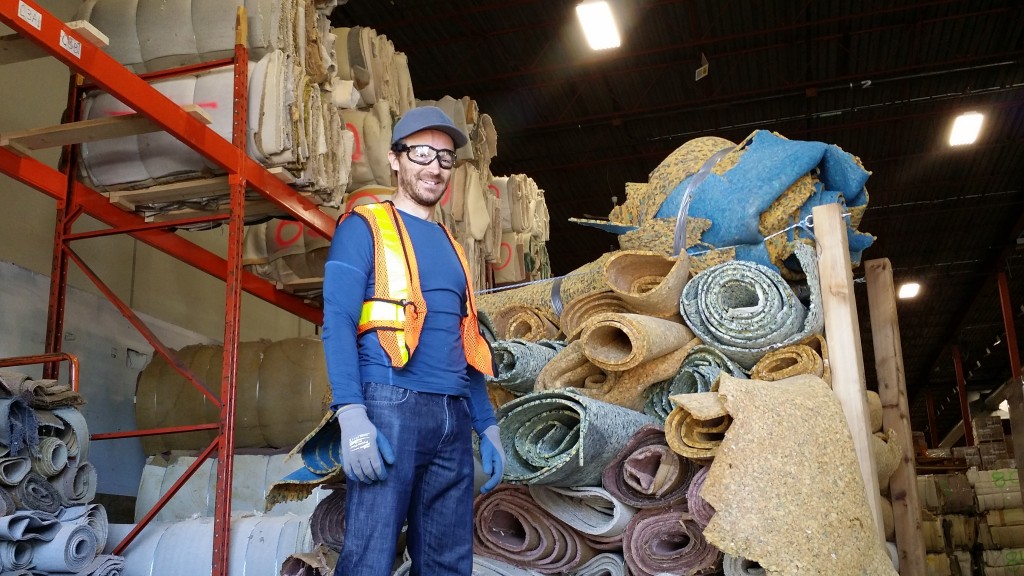
/in Carpet Recycling, Commercial Rubbish Removal and Recycling, Plastic Recylcing, Property Clean-up Services, Recycling, Renovation Waste/by Green Coast RubbishWe love to work closely with green conscious businesses who care as much the environment as we do. That’s why we’re really excited to have Pacific Carpet Recycling as a partner. They are the only carpet and underlay recycler in Vancouver, and they’re doing great work around the Lower Mainland.
Carpet is something that most people take for granted; not really giving it much thought until they are looking to renovate a space. But the amount of waste created from carpet being thrown into our landfills is mindblowing — as much as 80 million lbs are thrown into garbage dumps in Metro Vancouver alone! Even worse, it can take as long as 50 years for it to break down once it’s in there. But it doesn’t have to be this way. Being a petroleum-based product, many types of carpet and underlay are recyclable, and can be made into new flooring, clothing, furniture, auto parts, and other items we use on a daily basis.
In recent years, PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) carpet has gained popularity, because it’s manufactured using recycled pop bottles. In theory, this sounds like an excellent green alternative, but at the present time there are no effective means to recycle carpet once it is made from this material. If you are looking for the most environmentally mindful flooring, PCR suggests opting for Nylon carpeting instead, which is completely recyclable.
Though Pacific Carpet Recycling does not deal directly with the consumer public, Green Coast Rubbish has partnered exclusively with them, allowing us to remove the carpet from your home or business (and any other waste that you might need hauled away) and deliver it to PCR on your behalf. If you have any questions about recycling carpet, or the work we do at Green Coast Rubbish, please never hesitate to contact us.
Plastics: A Complex Issue
/in Plastic Recylcing, Recycling, Uncategorized/by Green Coast RubbishPlastics can be found in every aspect of our lives, and its widespread use has changed us as a society. On one hand, it has allowed many products to be manufactured more quickly and inexpensively; on the other, the environmental repercussions have been significant.
The amount of waste produced from plastics has created many complex issues, including negatively impacting the health of our oceans. Tidal currents cause discarded plastics to collect in many areas, where they are consumed by fish, mammals, and birds — trickling down into every part of the food chain (including humans). Between 60-80% of all debris found in the water are plastic — there’s a floating mass in the Pacific Ocean approximately the size of Texas. And because plastics are an extremely durable material, they can take decades to breakdown once they are disposed, meaning they just accumulate in our landfills. Since the 1950’s, over a billion tonnes of plastics have been thrown away. This number is almost incomprehensible to most of us.
Thankfully, things are slowly beginning to change. Advancements in plastics technology have made some forms of plastics biodegradable — allowing them to disintegrate when exposed to water, or sunlight. Recycling programs have expanded in many cities to include more options for processing.

More recently, innovative businesses like The Plastic Bank have developed, placing more value on plastics — in turn encouraging the collection, recycling, and reuse of more of these materials in developing countries. All these steps begin to address the issues of how to deal with the overabundance of plastics in our country, and throughout the world.
At Green Coast Rubbish we work together with the North Shore Recycling Drop-off Depot for soft as well as numbered plastics, and for blended plastics and PVC piping we utilize Blue Planet Recycling Ltd. In 2013, we helped keep over 2 tonnes of plastics from our landfills and oceans. We were happy to see that Vancouver has recently changed its blue box program in May 2014 to include clamshell packaging (and more).
There are many kinds of plastics, and the rules of what can and can’t be recycled can get confusing. The David Suzuki Foundation has an excellent list which explains the differences, and various types.
Though recycling is an excellent way to help keep more plastic waste out of our landfills, ultimately, being mindful at the point of sale is important too. Plastic items will be stamped with a number on the bottom (designating how & if that material can be recycled). If there is no number present, there is a good chance that item will end up in a landfill. Being informed about your purchases before you buy is the best way to ensure you’re choosing items that are good for you, while still being good to our environment. Reduce when you can. Reuse what you’re able. Recycle when it’s done. Our environment will thank you for it!